is a program that uses an objects attributes to determine what group or class it belongs to
What is object-oriented programming?
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a computer programming model that organizes software pattern effectually data, or objects, rather than functions and logic. An object tin can exist divers as a data field that has unique attributes and beliefs.
OOP focuses on the objects that developers want to dispense rather than the logic required to manipulate them. This arroyo to programming is well-suited for programs that are large, complex and actively updated or maintained. This includes programs for manufacturing and blueprint, as well equally mobile applications; for example, OOP can be used for manufacturing system simulation software.
The system of an object-oriented programme also makes the method beneficial to collaborative development, where projects are divided into groups. Additional benefits of OOP include code reusability, scalability and efficiency.
The first footstep in OOP is to collect all of the objects a programmer wants to manipulate and place how they relate to each other -- an exercise known as data modeling.
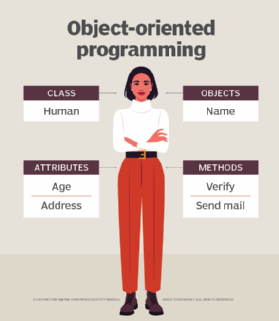
Examples of an object can range from physical entities, such as a human being who is described by properties similar name and address, to minor estimator programs, such as widgets.
Once an object is known, information technology is labeled with a class of objects that defines the kind of information it contains and whatsoever logic sequences that tin can manipulate information technology. Each distinct logic sequence is known equally a method. Objects can communicate with well-divers interfaces called messages.
What is the construction of object-oriented programming?
The structure, or building blocks, of object-oriented programming include the post-obit:
- Classes are user-defined information types that act equally the blueprint for private objects, attributes and methods.
- Objects are instances of a class created with specifically defined data. Objects tin correspond to existent-world objects or an abstract entity. When class is defined initially, the description is the simply object that is defined.
- Methods are functions that are defined within a class that describe the behaviors of an object. Each method contained in class definitions starts with a reference to an instance object. Additionally, the subroutines independent in an object are called instance methods. Programmers utilise methods for reusability or keeping functionality encapsulated inside one object at a time.
- Attributes are defined in the class template and stand for the state of an object. Objects will accept data stored in the attributes field. Class attributes belong to the class itself.
What are the primary principles of OOP?
Object-oriented programming is based on the post-obit principles:
- Encapsulation . This principle states that all important data is contained inside an object and only select information is exposed. The implementation and state of each object are privately held inside a defined class. Other objects do non take admission to this grade or the dominance to make changes. They are simply able to call a listing of public functions or methods. This feature of information hiding provides greater programme security and avoids unintended data corruption.
- Abstraction . Objects only reveal internal mechanisms that are relevant for the use of other objects, hiding any unnecessary implementation lawmaking. The derived course can have its functionality extended. This concept can aid developers more easily make additional changes or additions over time.
- Inheritance . Classes can reuse code from other classes. Relationships and subclasses between objects can be assigned, enabling developers to reuse common logic while nevertheless maintaining a unique hierarchy. This property of OOP forces a more thorough data analysis, reduces evolution fourth dimension and ensures a college level of accuracy.
- Polymorphism . Objects are designed to share behaviors and they can take on more one form. The programme will make up one's mind which meaning or usage is necessary for each execution of that object from a parent form, reducing the demand to duplicate code. A child class is and so created, which extends the functionality of the parent grade. Polymorphism allows different types of objects to laissez passer through the same interface.
What are examples of object-oriented programming languages?
While Simula is credited as being the kickoff object-oriented programming language, many other programming languages are used with OOP today. But some programming languages pair with OOP better than others. For instance, programming languages considered pure OOP languages care for everything as objects. Other programming languages are designed primarily for OOP, but with some procedural processes included.
For instance, popular pure OOP languages include:
- Red
- Scala
- JADE
- Emerald
Programming languages designed primarily for OOP include:
- Java
- Python
- C++
Other programming languages that pair with OOP include:
- Visual Bones .NET
- PHP
- JavaScript
What are the benefits of OOP?
Benefits of OOP include:
- Modularity. Encapsulation enables objects to exist self-contained, making troubleshooting and collaborative evolution easier.
- Reusability. Code can be reused through inheritance, meaning a team does non have to write the same lawmaking multiple times.
- Productivity. Programmers can construct new programs quicker through the use of multiple libraries and reusable code.
- Easily upgradable and scalable. Programmers can implement system functionalities independently.
- Interface descriptions . Descriptions of external systems are simple, due to message passing techniques that are used for objects communication.
- Security. Using encapsulation and abstraction, complex code is hidden, software maintenance is easier and internet protocols are protected.
- Flexibility. Polymorphism enables a single function to suit to the form it is placed in. Different objects tin besides pass through the same interface.
Criticism of OOP
The object-oriented programming model has been criticized by developers for multiple reasons. The largest business organisation is that OOP overemphasizes the data component of software evolution and does not focus enough on computation or algorithms. Additionally, OOP code may be more than complicated to write and take longer to compile.
Alternative methods to OOP include:
- Functional programming. This includes languages such as Erlang and Scala, which are used for telecommunications and fault tolerant systems.
- Structured or modular programming. This includes languages such as PHP and C#.
- Imperative programming . This culling to OOP focuses on role rather than models and includes C++ and Java.
- Declarative programming . This programming method involves statements on what the job or desired outcome is but non how to achieve information technology. Languages include Prolog and Lisp.
- Logical programming. This method, which is based by and large in formal logic and uses languages such equally Prolog, contains a set of sentences that limited facts or rules about a problem domain. It focuses on tasks that can benefit from rule-based logical queries.
Most advanced programming languages enable developers to combine models, considering they can be used for different programming methods. For example, JavaScript can be used for OOP and functional programming.
Developers who are working with OOP and microservices tin address common microservices issues by applying the principles of OOP .
This was last updated in July 2021
Continue Reading About object-oriented programming (OOP)
- Scala: Lightweight functional programming for Java
- Cull the all-time programming linguistic communication for DevOps workflows
- To address microservices issues, turn to OOP principles
- 10 of the best programming languages to learn in 2020
- A breakdown of object-oriented programming concepts
Dig Deeper on Awarding development and design
-

A breakdown of object-oriented programming concepts
-

A comparison of 6 tiptop programming languages
-

Scala: Lightweight functional programming for Java
-

grade diagram
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchapparchitecture/definition/object-oriented-programming-OOP


0 Response to "is a program that uses an objects attributes to determine what group or class it belongs to"
Post a Comment